As the world shifts towards sustainability, the demand for green energy is increasing. Green energy, often used interchangeably with renewable energy, plays a crucial role in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. But what exactly is green energy, and how does it differ from other renewable energy sources? In this article, we will explore the fundamentals of green energy, its types, benefits, challenges, and why it is essential for a sustainable future.
What is Green Energy?
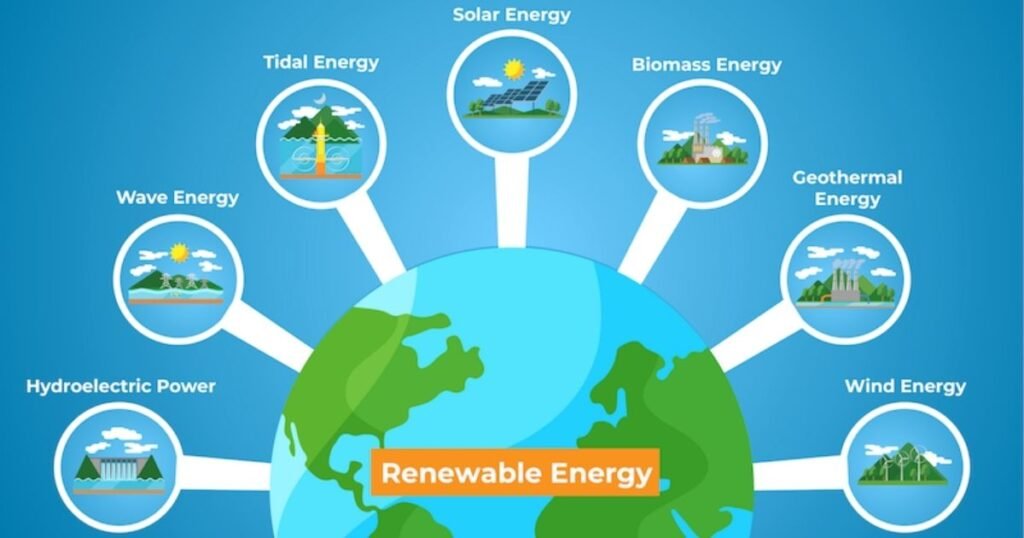
Green energy, also known as green power, refers to energy sources that have the highest environmental benefits and are derived from naturally replenishing resources. These energy sources produce little to no carbon emissions and have minimal environmental impact. According to the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA), green energy includes power generated from solar, wind, geothermal, biogas, low-impact hydroelectric, and certain eligible biomass sources.
Difference Between Renewable and Green Energy
While all green energy sources are renewable, not all renewable energy sources are considered green. The distinction lies in environmental impact. For example:
- Green Energy: Solar, wind, and low-impact hydroelectric are considered green because they have minimal environmental footprints.
- Renewable Energy: While biomass and large-scale hydroelectric power are renewable, their environmental impact (e.g., deforestation, habitat disruption) can prevent them from being classified as truly green.
By choosing green energy, individuals and businesses support investments in clean, sustainable energy projects that contribute to a healthier planet.
How Does Green Energy Work?
Green energy is generated through sustainable processes that do not deplete natural resources or contribute to environmental harm. The process varies based on the energy source:
1. Solar Energy
Solar panels use photovoltaic cells to convert sunlight into electricity. Excess energy can be stored in batteries or fed into the grid.
2. Wind Energy
Wind turbines capture kinetic energy from wind and convert it into electrical power. Offshore and onshore wind farms contribute significantly to global electricity supply.
3. Hydroelectric Power
Water movement, typically from rivers or dams, drives turbines to generate electricity. Low-impact hydroelectric plants are preferred due to their minimal ecological disruption.
4. Geothermal Energy
Heat from the Earth’s core is harnessed to produce steam, which drives turbines to generate electricity. Geothermal power plants provide a consistent energy supply.
5. Biomass and Biogas
Organic waste, including agricultural residues and food waste, is converted into biofuels or biogas through combustion or anaerobic digestion, reducing landfill waste while generating energy.
Benefits of Green Energy
1. Reduces Carbon Emissions
Green energy significantly lowers greenhouse gas emissions compared to fossil fuels, helping mitigate climate change.
2. Creates Jobs and Economic Growth
The green energy sector generates millions of jobs worldwide, boosting local economies and driving technological advancements.
3. Improves Public Health
Unlike fossil fuels, green energy sources do not release harmful pollutants, reducing respiratory diseases and other health risks.
4. Energy Security and Independence
By utilizing local renewable resources, countries can reduce their reliance on imported fossil fuels and enhance energy security.
5. Sustainable and Abundant
Renewable energy sources are naturally replenishing, ensuring a sustainable energy future for generations to come.
Challenges of Green Energy
Despite its benefits, green energy faces challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption:
1. High Initial Costs
Setting up renewable energy infrastructure, such as solar farms and wind turbines, requires significant investment.
2. Intermittency Issues
Solar and wind energy depend on weather conditions, making energy storage solutions crucial.
3. Land and Resource Requirements
Large-scale renewable energy projects require land and natural resources, which can lead to ecological concerns.
4. Storage and Distribution
Efficient storage technologies and an upgraded power grid are necessary to manage green energy supply effectively.
Future of Green Energy
Advancements in technology, energy storage, and government policies are accelerating the global transition to green energy. Innovations in battery storage, smart grids, and hydrogen fuel cells are making renewable energy more efficient and accessible. As awareness grows and investments increase, green energy will play a central role in shaping a sustainable world for future generations.
Conclusion
Green energy is the key to a sustainable future. With advancements in renewable energy technologies, the shift towards green power is becoming more accessible and cost-effective. By choosing green energy, individuals and businesses can contribute to a cleaner environment and a more resilient energy system. Governments, corporations, and individuals must work together to support and adopt green energy solutions to combat climate change and secure a cleaner future for the planet.