🔍 Table of Contents
- Introduction
- What is Green Hydrogen?
- Types of Hydrogen Based on Production
- How is Green Hydrogen Produced?
- Advantages of Green Hydrogen
- Applications of Green Hydrogen
- Challenges and Limitations
- Global Developments and the Future
- Real-World Case Studies
- FAQs about Green Hydrogen
- Conclusion
🔍 Introduction
As the world moves toward sustainable energy solutions, Green Hydrogen has emerged as a promising alternative to fossil fuels. Hydrogen is a versatile and abundant energy carrier, but its environmental impact varies based on its production method.
Green Hydrogen, created using renewable energy, results in zero carbon emissions, making it crucial to the future of decarbonized global economies. From powering industries to enabling clean transportation, Green Hydrogen is the cornerstone of a resilient, low-carbon energy system.
📂 Also read: Energy Transition in Oil & Gas – A Process Safety Perspective
💧 What is Green Hydrogen?
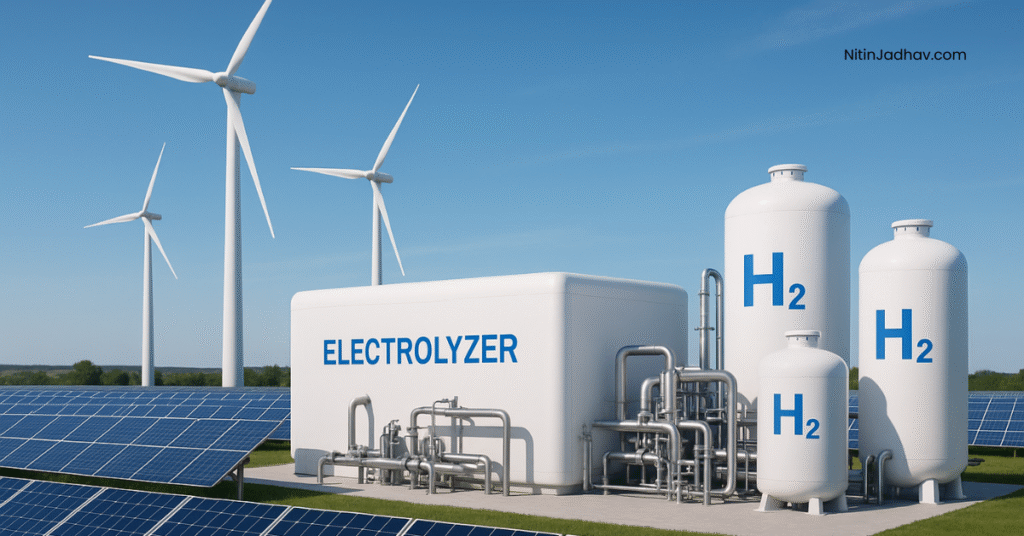
Green Hydrogen is hydrogen gas (H₂) produced via the electrolysis of water using electricity from renewable energy sources like solar, wind, or hydro. Unlike Grey or Blue Hydrogen, it does not produce carbon dioxide during production.
This makes it the most environmentally sustainable hydrogen type, suitable for long-term global energy strategies.
📒 Types of Hydrogen Based on Production
| Type | Feedstock & Method | CO₂ Emissions |
|---|---|---|
| Green | Electrolysis + Renewable Electricity | ❌ None |
| Grey | Natural Gas/Coal + SMR | ✅ High |
| Blue | Natural Gas + Carbon Capture | ⚠️ Moderate |
| Turquoise | Methane Pyrolysis → Solid Carbon | ♻️ Byproduct: Carbon |
📚 Learn More: Process Safety in Hydrogen Storage
⚙️ How is Green Hydrogen Produced?
1. Electrolysis of Water
Electrolysis splits H₂O into hydrogen (H₂) and oxygen (O₂) using renewable electricity in an electrolyzer.
Electrolyzer Components:
- Anode (+): Releases O₂
- Cathode (–): Produces H₂
- Electrolyte: Transfers ions
Reaction Formula:
2H₂O → 2H₂ + O₂ (using electricity)
2. Renewable Energy Inputs
- 🌞 Solar Power: PV panels for clean electricity
- 🌬️ Wind Energy: Onshore and offshore turbines
- 💧 Hydropower: Kinetic energy from water flows
3. Hydrogen Storage & Transportation
- Compressed Gas: In high-pressure tanks
- Liquid Hydrogen: Cooled to -253°C
- Chemical Carriers: Ammonia (NH₃), Methanol (CH₃OH)
📂 See Also: Hydrogen Safety and Explosion Risks
✅ Advantages of Green Hydrogen
- Zero Emissions: No CO₂ released during production
- Energy Storage: Stores surplus renewable energy
- Versatility: Usable in transport, industry, and power sectors
- Reduced Fossil Dependence: Helps phase out coal and gas
- Energy Security: Local renewable generation reduces imports
🚀 Applications of Green Hydrogen
1. Transportation
- Fuel Cell Vehicles: Buses, Trucks, Trains
- Marine Vessels: Hydrogen ferries and ships
- Aviation: Hydrogen propulsion aircraft
2. Industrial Use
- Steel, cement, fertilizer, and chemical sectors
- Clean substitute for coal or natural gas
3. Power Generation
- Fuel cells for electricity
- Hydrogen-natural gas blending in turbines
4. Residential Heating
- Mixed with natural gas in pipelines
5. Grid-Level Energy Storage
- Stores excess solar/wind energy for off-peak use
⚠️ Challenges and Limitations
1. High Cost
Electrolyzers and renewable power are still expensive.
2. Infrastructure Deficit
Lack of pipelines, refueling stations, and storage.
3. Energy Efficiency Loss
Hydrogen conversion and use lose 30-40% of input energy.
4. Water Consumption
Electrolysis requires large amounts of clean water.
5. Scale-up Challenges
Requires mass production of electrolyzers and renewables.
📂 Also read: Fire and Explosion Risks in Hydrogen Systems
🌍 Global Developments and the Future
1. Government Initiatives
- India: National Green Hydrogen Mission – ₹19,744 crore allocation
- EU: 40 GW Electrolyzer target by 2030
- USA: Hydrogen hubs under Infrastructure Law
2. Technology Trends
- PEM & AEM Electrolyzers
- Solid-state hydrogen storage
- Hydrogen smart grids
3. Declining Costs
- Solar/wind prices dropping globally
- Electrolyzer manufacturing scaling up
4. Integration with Clean Tech
- Coupled with solar parks and wind farms
- Power-to-hydrogen microgrids
🏛️ Real-World Case Studies
🇩🇪 Germany: HyDeal Ambition
Plans to deliver 3 million tonnes of green hydrogen annually by 2030.
🇮🇳 India: Reliance & Adani Projects
Reliance Industries and Adani Green Energy are investing in massive electrolyzer and hydrogen storage capacity.
🇺🇸 USA: Clean Hydrogen Hubs
The US DOE plans to develop regional hydrogen hubs connecting industries and power plants.
🤔 FAQs about Green Hydrogen
Q1: Is Green Hydrogen completely carbon-free?
Yes, provided the electricity used comes entirely from renewable sources.
Q2: How is Green Hydrogen stored safely?
Storage is done via high-pressure tanks, liquefaction, or hydrogen carriers like ammonia.
Q3: What is the current cost of Green Hydrogen?
Varies globally, typically around $3–7 per kg, expected to drop below $2/kg by 2030.
Q4: Can Green Hydrogen replace petrol or diesel?
Yes, especially in heavy transport and marine sectors where battery-electric may not be viable.
Q5: Is water scarcity a barrier to Green Hydrogen?
Yes, electrolysis requires significant fresh water, which may limit deployment in arid regions.
🔠 Conclusion
Green Hydrogen is not just a fuel – it’s a transformational clean energy vector. Its ability to decarbonize hard-to-abate sectors and store renewable energy makes it indispensable for a net-zero future.
Although challenges like cost, infrastructure, and efficiency persist, government policies, corporate investments, and technology breakthroughs are accelerating its global adoption.