Introduction
In the high-risk environments of oil & gas, petrochemicals, refineries, and chemical plants, one unexpected deviation in process parameters can result in catastrophic consequences. This could include toxic releases, fires, explosions, or even full-blown plant shutdowns. That’s why risk identification is the first and most vital step in preventing industrial disasters.
At the heart of process safety lies HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) — a powerful, structured methodology that identifies potential hazards and operability problems before they become incidents.
This article explains the importance of HAZOP, its methodology, its role in the process safety lifecycle, and how industries can integrate it effectively to save lives, reduce downtime, and ensure compliance.
👉 Internal Link: HAZOP Study – A Detailed Guide
What is HAZOP?
HAZOP (Hazard and Operability Study) is a structured, systematic, team-based analysis technique used to identify potential hazards and operability issues in process systems. It involves:
- Reviewing process design and flow
- Breaking it into manageable nodes
- Using structured guidewords to identify deviations
- Analyzing causes, consequences, and safeguards
Developed by ICI (Imperial Chemical Industries) in the 1960s, HAZOP has become the industry gold standard in hazard identification.
Why is HAZOP Important?
HAZOP is crucial because:
✅ It identifies “unknown knowns”
Designers and engineers may miss interactions or edge cases that can lead to failure.
✅ It’s proactive, not reactive
Unlike incident investigations, HAZOP happens before incidents occur.
✅ It strengthens the safety culture
Cross-functional team involvement increases risk awareness across departments.
✅ It ensures compliance with global regulations
Regulators like OSHA, HSE (UK), and PESO (India) require hazard identification studies as part of PSM.
👉 Internal Link: Process Safety Studies in Oil & Gas
Where HAZOP Fits in the Process Safety Lifecycle
HAZOP typically occurs after P&ID finalization but before commissioning. It also supports:
- Management of Change (MOC)
- Pre-startup safety reviews
- 5-year revalidation (as per OSHA)
- Process optimization and risk mitigation
It is also a critical input for:
- SIL Study
- Fire and Gas Detector Mapping
- Emergency Response Planning
- LOPA (Layer of Protection Analysis)
- QRA (Quantitative Risk Assessment)
👉 Internal Link: SIL Study – A Comprehensive Guide
HAZOP Methodology
Step 1: Define Study Scope
- Establish goals, systems to be reviewed
- Gather P&IDs, PFDs, process descriptions
Step 2: Break Process into Nodes
A node is a section of the process (e.g., reactor inlet, pump discharge) with identifiable parameters.
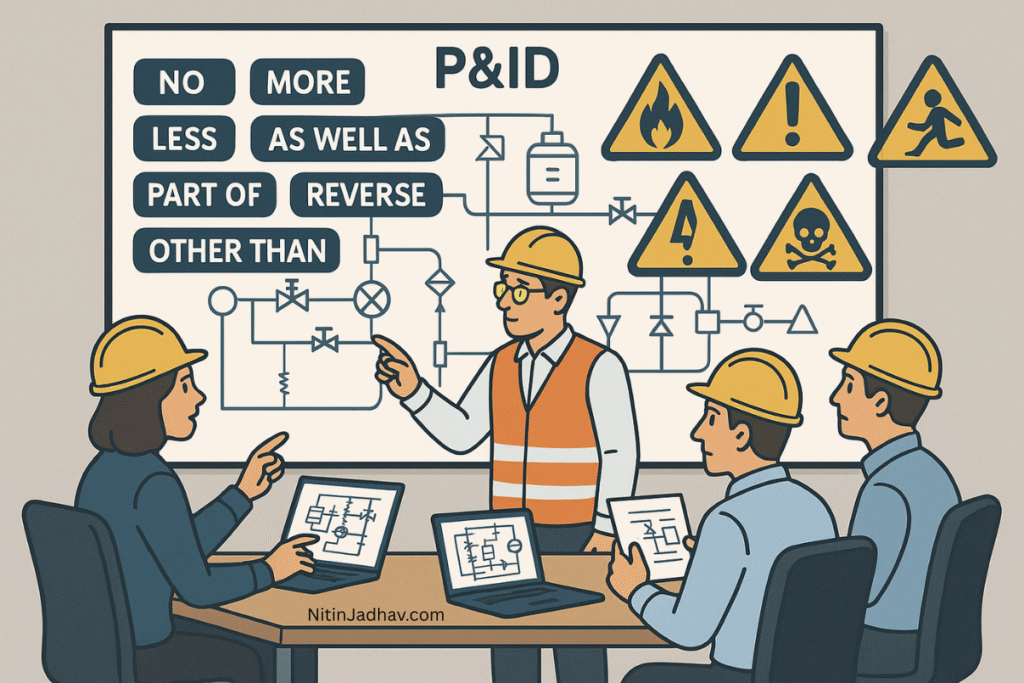
Step 3: Apply Guidewords to Each Parameter
| Parameter | Guidewords |
|---|---|
| Flow, Pressure, Temperature, Level | No, More, Less, Reverse, Other than, As well as |
Step 4: Team Discussion
For each deviation:
- Identify possible causes
- Determine consequences
- Assess existing safeguards
- Recommend corrective actions if required
Step 5: Documentation
All discussions and recommendations are logged in standardized HAZOP worksheets.
HAZOP Table Example
| Node | Deviation | Cause | Consequence | Safeguard | Recommendation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reactor Feed Line | No Flow | Pump failure | Reaction not initiated | Flow alarm | Add standby pump |
Benefits of HAZOP
1. Early Hazard Identification
Before plant construction or operation, you already know the risk hotspots.
2. Design Improvement
HAZOP highlights design weaknesses like improper interlocks, sizing issues, or control philosophy gaps.
3. Risk Prioritization
HAZOP gives clarity on high, medium, and low risks, enabling resource optimization.
4. Enhanced Regulatory Compliance
Meets global expectations under OSHA PSM, Seveso III Directive, and Indian MSIHC rules.
5. Supports SIL & QRA Studies
Outputs such as initiating events and severity data feed into quantitative assessments.
When Should HAZOP Be Conducted?
| Phase | Purpose |
|---|---|
| FEED Stage | Early hazard screening (Pre-HAZOP or HAZID) |
| Detailed Design | Full-scale HAZOP |
| MOC Reviews | Assessing impact of design changes |
| 5-Year Revalidation | Required by OSHA and global PSM standards |
| Post-Incident | Optional – to reassess weaknesses in design/response |
Team Structure for HAZOP
| Role | Responsibility |
|---|---|
| Facilitator | Guides session, applies methodology |
| Process Engineer | Provides design intent |
| Instrumentation Engineer | Explains alarms, interlocks |
| Operations Expert | Offers practical plant insight |
| Maintenance | Highlights potential equipment failure |
| HSE Representative | Ensures hazard focus remains sharp |
Integration with Other Safety Studies
HAZOP plays a central role in the safety ecosystem.
| Study | Dependency on HAZOP |
|---|---|
| SIL Study | Uses HAZOP-identified scenarios for demand rate |
| QRA | HAZOP causes feed into frequency estimates |
| F&G Mapping | Locations and triggers for detector placement |
| EERA | Emergency scenarios validated through HAZOP outputs |
👉 Internal Link: FERA – Fire and Explosion Risk Analysis
HAZOP in Indian and Global Context
- In India, PESO, OISD, and state regulators often mandate HAZOPs for LPG, POL, chemical, and pharma installations.
- Globally, organizations like Shell, BP, ExxonMobil require HAZOP as part of their stage-gate engineering process.
Common Pitfalls in HAZOP and How to Avoid Them
| Pitfall | Solution |
|---|---|
| Lack of preparation | Ensure up-to-date P&IDs, process data |
| Poor team dynamics | Pre-session training and role clarification |
| No follow-up on recommendations | Use digital action tracking tools |
| Repetitive sessions | Assign nodes efficiently; avoid fatigue |
| Ignoring human factors | Include ergonomic and behavioral inputs |
HAZOP Tools and Software
| Tool | Key Features |
|---|---|
| PHA Pro | HAZOP, LOPA, Risk Matrix documentation |
| PHAWorks | Real-time action tracking |
| BowTieXP | Visual risk modeling with bowties |
| Intelex / Enablon | Integrated EHS & compliance platform |
HAZOP Case Study – Ethylene Storage and Transfer Unit
Observations:
- High flow deviation → PSV lifting frequently
- Reverse flow scenario → Potential for backpressure on compressor
- Low level in knock-out drum → Risk of dry running
Recommendations:
- Recalculate PSV sizing
- Install NRV in return line
- Add low-level trip to safeguard pump
Result: Design modifications implemented before commissioning; 3-year incident-free operation.
FAQs
Q1: Is HAZOP mandatory?
Yes. Under OSHA 29 CFR 1910.119 (USA) and Indian MSIHC Rules, HAZOP is part of compliance for hazardous industries.
Q2: Can HAZOP be done remotely?
Yes. Many companies now conduct remote HAZOPs using MS Teams, Zoom, and digital whiteboards with positive results.
Q3: How long does HAZOP take?
Depends on size; a large refinery unit can take 2–3 weeks. Small units take 2–5 days.
Q4: How is HAZOP different from HAZID?
HAZID is a broad-brush hazard identification tool used in early design. HAZOP is a deep dive into deviations during design or operation.
Conclusion
The significance of HAZOP cannot be overstated. It is one of the most effective and widely accepted tools in process safety and hazard management. A well-executed HAZOP helps you:
- Uncover hidden hazards
- Improve design reliability
- Strengthen operational control
- Achieve compliance with safety norms
- Foster a culture of safety across your organization
Integrating HAZOP at the right project stages ensures not only regulatory alignment but also sustainable and resilient operations.
For every process safety professional, plant designer, or operator, HAZOP is not a formality—it is a lifesaving tool.