Understanding your salary slip is one of the most essential aspects of personal finance. It is not just a piece of paper or a PDF sent by your HR department—it is a detailed breakdown of how much you earn, how much tax you pay, and what benefits you receive. If you are working in India in 2025, knowing how to read your salary slip can help you manage your finances better, plan your taxes, and ensure you are being paid correctly.
In this guide, we will explain every section of the salary slip, decode important terms, highlight changes as per the latest financial year (2025), and provide tips to optimize your take-home pay.
1. Why Understanding Your Salary Slip Matters in 2025
A salary slip (also known as a payslip) is an official document issued by your employer every month. It acts as proof of your employment and details your earnings, deductions, and net pay.
Key reasons to understand your salary slip:
- Financial Planning: Helps you track your income and budget expenses effectively.
- Tax Compliance: Ensures you know exactly how much income tax is being deducted and how to claim deductions under the Income Tax Act.
- Loan Applications: Serves as proof of income for home loans, personal loans, or credit cards.
- Error Detection: Helps you spot discrepancies in your pay structure.
- Salary Negotiations: Understanding your CTC structure helps you negotiate better during job changes.
How to Create a Monthly Budget in India
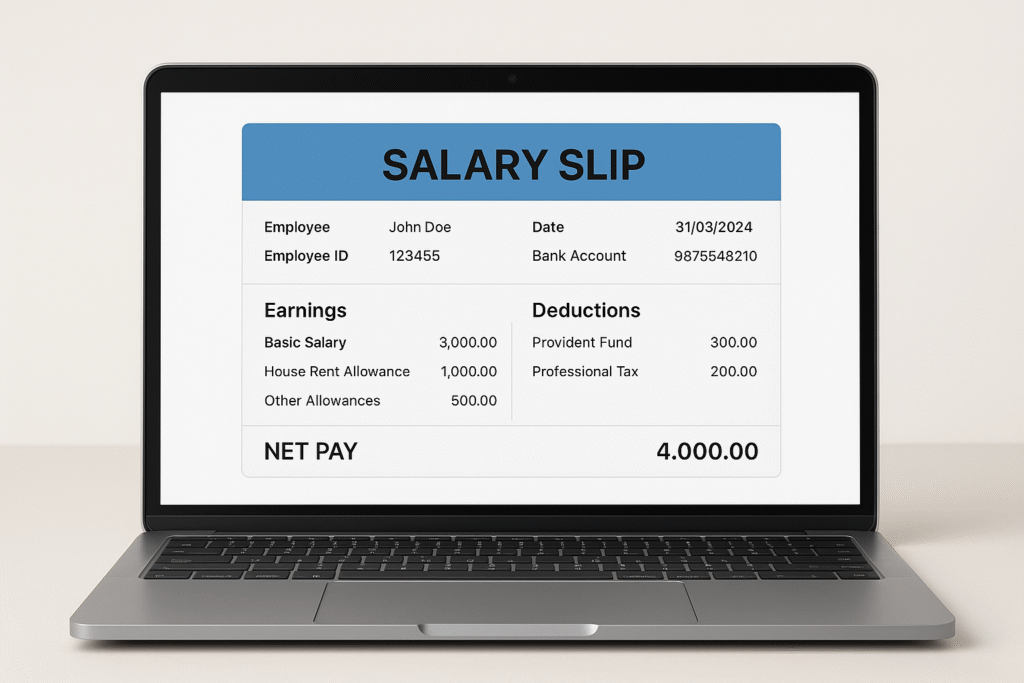
2. Salary Slip Structure in India (2025 Format)
Salary slips in India are usually divided into three main sections:
- Earnings (Income Components)
- Deductions
- Net Pay
Most companies issue digital payslips in PDF format, while some government employees still receive printed versions. In 2025, HRMS (Human Resource Management System) portals make it easy to download monthly salary slips anytime.
3. Earnings Section – Understanding the Components
The earnings section lists all the allowances and basic salary you receive. Let us break down the common components:
a) Basic Salary
- Definition: The fixed component of your pay, usually 35–50% of your CTC.
- Tax Impact: Fully taxable.
- Importance: Determines other benefits like Provident Fund (PF), gratuity, and retirement contributions.
b) Dearness Allowance (DA) – Mostly for Government Employees
- Definition: Paid to offset inflation.
- Tax Impact: Fully taxable.
- Note: In private companies, DA may be merged into basic or other allowances.
c) House Rent Allowance (HRA)
- Definition: Paid to cover rental expenses if you live in a rented house.
- Tax Impact: Eligible for HRA tax exemption under Section 10(13A) if you pay rent.
- Tip: Submit rent receipts to your employer for tax benefits.
d) Conveyance / Transport Allowance
- Definition: Provided for commuting expenses.
- Tax Impact: Fully taxable after removal of the old conveyance exemption in the 2018 budget.
e) Special Allowance
- Definition: Flexible pay component used to adjust total salary.
- Tax Impact: Fully taxable.
f) Performance Bonus / Incentives
- Definition: Variable pay based on your performance and company targets.
- Tax Impact: Fully taxable in the year it is received.
g) Other Allowances (2025 Trend)
With remote work still prevalent, companies in 2025 often include:
- Internet Allowance
- Remote Work Setup Allowance
- Learning & Development Stipend
4. Deductions Section – Where Your Money Goes
The deductions section shows how much is subtracted from your gross earnings.
a) Employee Provident Fund (EPF)
- Contribution: 12% of your basic salary.
- Benefit: Long-term retirement savings with tax-free interest.
- Tip: Keep track of your UAN (Universal Account Number) for easy PF balance checks.
b) Professional Tax (PT)
- Definition: State-level tax deducted monthly.
- Amount: Varies from ₹200–₹300 per month depending on state rules.
- Note: Not applicable in some states like Delhi and Haryana.
c) Tax Deducted at Source (TDS)
- Definition: Income tax deducted based on your projected annual income.
- Tip: Submit your investment proofs before the deadline to reduce TDS.
d) Health Insurance Premium
- Many companies provide group health insurance, with the premium partly deducted from salary.
e) Other Deductions
- Loan EMIs (if repaid via salary deduction)
- Voluntary Provident Fund (VPF) contributions
- Meal Coupons or Sodexo deductions
5. Key Salary Slip Terms You Must Know in 2025
CTC (Cost to Company)
- Definition: Total annual cost the employer spends on you, including salary, benefits, and bonuses.
- Misconception: CTC is not your take-home pay.
Gross Salary
- Definition: Salary before deductions.
Net Salary / Take-Home Pay
- Definition: Amount credited to your bank account after all deductions.
6. Tax Implications and Budget 2025 Changes
The Union Budget 2025 has slightly modified income tax slabs and standard deduction limits.
- Standard Deduction: Increased to ₹75,000 for salaried employees.
- Tax Regime Choice: You can opt for the new regime (lower rates, fewer exemptions) or old regime (higher rates, more exemptions like HRA, LTA).
- HRA Claims: Still available in old regime.
For more visit : Income Tax Department official website
7. How to Read Your Salary Slip – Step-by-Step
- Check your name, employee code, and pay period for accuracy.
- Review earnings section to see if all components match your offer letter.
- Verify deductions and ensure TDS matches your tax planning.
- Calculate gross salary by adding all earnings.
- Subtract deductions to find your net pay.
- Check leave encashment or arrears if applicable.
8. Common Salary Slip Mistakes to Watch For
- Wrong calculation of HRA exemption
- Incorrect PF deduction percentage
- Missing bonus or incentive
- Over-deduction of TDS due to unsubmitted investment proofs
9. Tips to Optimize Your Take-Home Salary in 2025
- Opt for tax-saving allowances like meal vouchers, internet reimbursement, and travel claims.
- Submit rent and investment proofs early to avoid excess TDS.
- Negotiate basic-to-allowance ratio during salary discussions to optimize tax.
- Use Section 80C, 80D, and 80G deductions to lower taxable income.
Internal link suggestion: Link to a future nitinjadhav.com article on “Best Tax Saving Options in India for Salaried Employees”.
10. Digital Salary Slips and Security in 2025
With most payslips issued online via HR portals or email:
- Always download and store monthly copies for loan applications or tax filing.
- Avoid sharing salary slips on unsecured platforms.
- Verify authenticity if requested by external agencies.
11. Sample Salary Slip Format (2025)
| Component | Amount (₹) |
|---|---|
| Basic Salary | 30,000 |
| HRA | 12,000 |
| Special Allowance | 8,000 |
| Performance Bonus | 5,000 |
| Gross Salary | 55,000 |
| EPF (12%) | -3,600 |
| Professional Tax | -200 |
| TDS | -4,000 |
| Net Salary | 47,200 |
12. Conclusion
Reading your salary slip in 2025 is no longer just an HR formality—it is an essential skill for financial empowerment. By understanding every component, checking deductions, and staying updated on tax rules, you can ensure that you get the most from your salary and plan your future effectively.
A well-informed employee is in a stronger position to negotiate salaries, save taxes, and achieve financial goals.
Final tip: Always keep at least the last 6 months’ salary slips safe—they are your key to loans, visa processing, and income verification.
External References:
- Income Tax Department of India – Official tax rules and slab rates
- EPFO Portal – Provident Fund balance check
- RBI Guidelines – Salary credit timelines